The World's Women 2010: Trends and Statistics
Chapter 4 - Work
Key findings
• Globally, women’s participation in the labour market remained steady in the two decades from 1990 to 2010, whereas that for men declined steadily over the same period; the gender gap in labour force participation remains considerable at all ages except the early adult years.
• Women are predominantly and increasingly employed in the services sector.
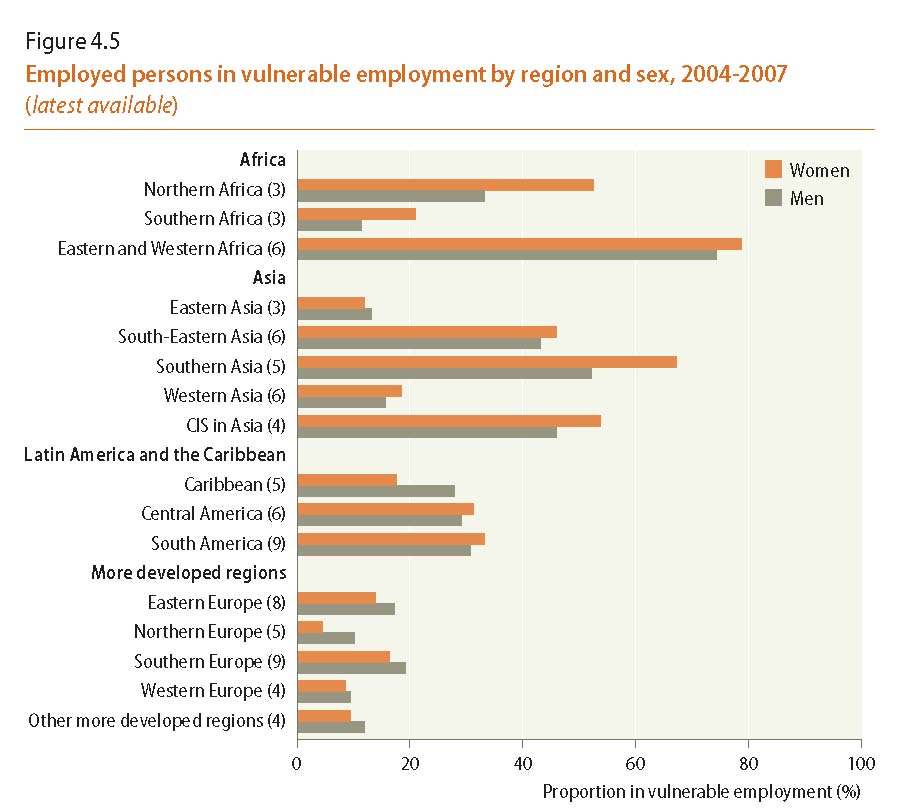
• Vulnerable employment – own-account work and contributing family work – is prevalent in many countries in Africa and Asia, especially among women.
• The informal sector is an important source of employment for both women and men in the less developed regions but more so for women.
• Occupational segregation and gender wage gaps continue to persist in all regions.
• Part-time employment is common for women in most of the more developed regions and some less developed regions, and it is increasing almost everywhere for both women and men.
• Women spend at least twice as much time as men on domestic work, and when all work – paid and unpaid – is considered, women work longer hours than men do.
• Half of the countries worldwide meet the new international standard for minimum duration of maternity leave – and two out of five meet the minimum standard for cash benefits – but there is a gap between law and practice, and many groups of women are not covered by legislation.
Download chapter 4
Full text (pdf)
English*: Color (1.40 MB), B/W (603 KB)
Statistical Annex:
Table 4.A to 4.D Excel (164 KB), Pdf (152 KB)
Download full report (pdf)
English*: Color (7.61 MB), B/W (7.7 KB) *For printing on a non-color printer, use B/W file for better results.Selected visual statistics (Click on the graph to enlarge)
Source: Computed by the United Nations Statistics Division based on country-level data from Statistics Sweden, UNECE, UNECLAC and national statistical offices (as of December 2009). Note: Unweighted averages; the numbers in brackets indicate the number of countries averaged.
Source:Computed by the United Nations Statistics Division based on data from ILO, Key Indicators of the Labour Market, 5th edition, table 3 (accessed in July 2009).
Note: Unweighted averages; the numbers in brackets indicate the number of countries averaged. The average for Eastern Asia does not include China. Western Asia excludes Armenia, Azerbaijan and Georgia; CIS in Asia includes the aforementioned countries plus Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan and Uzbekistan.